Ethiopia Sovereign Debt Market Overview, 2025 Edition
📊 Part of our Africa Bond Market Series
📅 Published: June 2025
💰 Exchange rate: Commercial Bank (cash mid-rate): ~132.8 ETB/USD
🟡 Conservative Expected GDP: USD 120 Billion
📩 Subscribe to Impala Market for weekly debt market updates
Executive Snapshot
Total Public Debt: ETB 5.14 trillion (~USD 38.74 billion)
Debt-to-GDP Ratio: ~32.5%
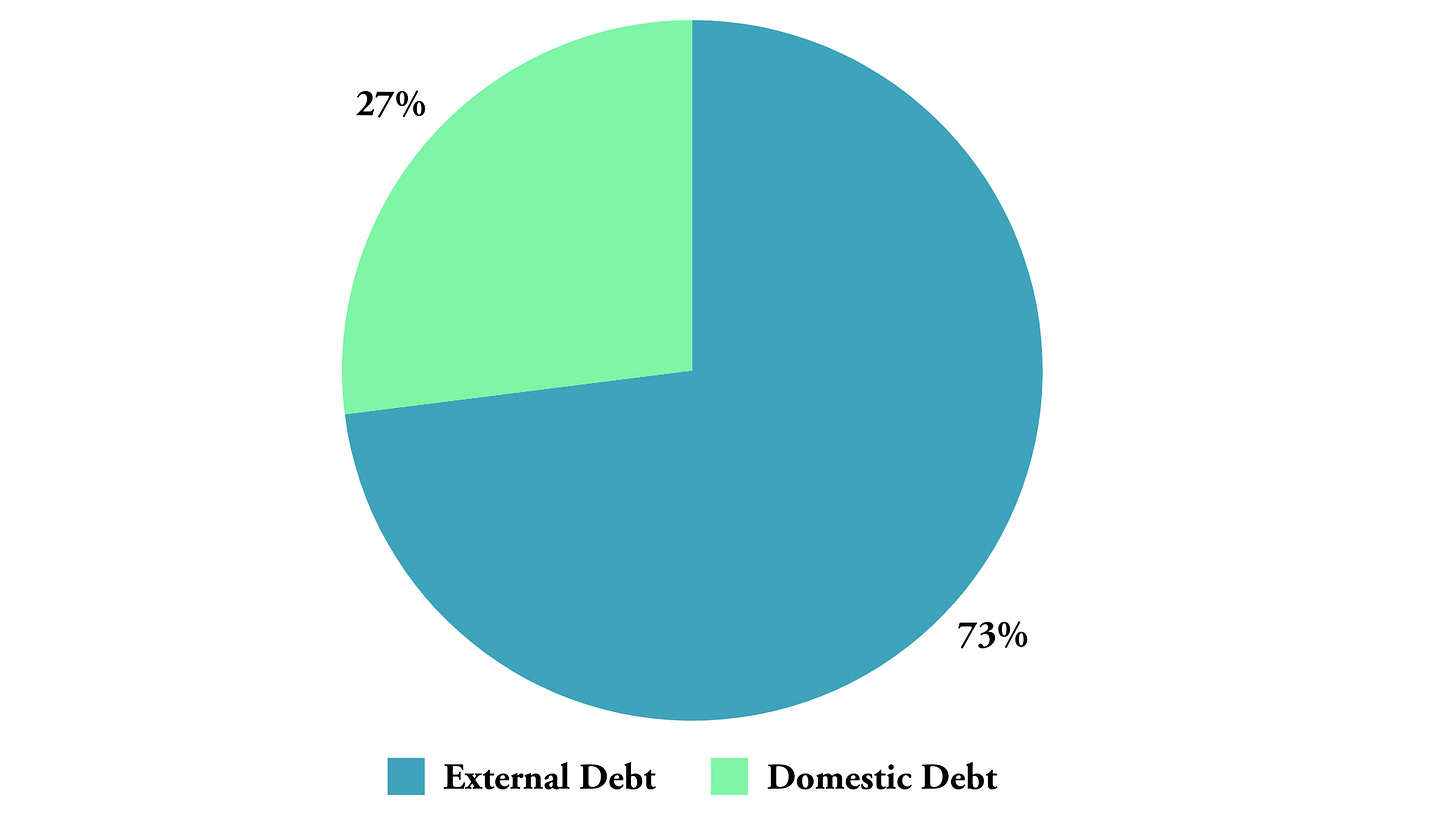
Debt Composition: ~73% external, ~27% domestic
Outlook: Ethiopia is transitioning from an opaque and centrally-managed debt environment to a structured sovereign debt market, supported by recent legal reforms, CSD infrastructure, and IMF-led fiscal discipline. Risks remain elevated due to FX shortages and ongoing debt restructuring.
1. Debt Market Structure
Total Public Debt Profile
External Debt: USD 28.2 billion
Domestic Debt: ETB 1.4 trillion (~USD 10.54 billion)
Debt Service-to-Revenue Ratio: ~30–35%
Source: Ministry of Finance – Ethiopia, IMF 2025
Legal & Institutional Framework
Capital Market Proclamation No. 1248/2021: Established legal foundation for securities issuance and OTC trading
Regulator: Ethiopian Capital Market Authority (ECMA)
CSD & Auction Agent: National Bank of Ethiopia (NBE)
Secondary Market Rules: ECMA Directive No. 1009/2024 governs OTC bond trading
2. Domestic Debt Instruments
Bonds are dematerialized and registered at NBE’s Central Securities Depository
Issuance primarily absorbed by state-owned banks and pension entities
Primary auctions conducted by commercial banks and brokers (primary dealers)
3. External Sovereign Debt
Ethiopia's external creditors include multilateral lenders like the IMF, World Bank, and AfDB, as well as bilateral partners such as China (its largest), France, and Kuwait. It also has a USD 1 billion Eurobond issued in 2024, which is currently under G20 Common Framework restructuring.
Insight: Ethiopia is gradually diversifying its creditor profile, with concessional debt giving way to more commercially-driven borrowing structures.
4. Investor Base
Domestic:
Commercial banks (e.g., Commercial Bank of Ethiopia)
State pension funds
Limited but growing interest from retail and private institutional investors
Foreign:
Eurobond holders
Some bilateral investor governments
Multilateral development partners
Insight: The local investor ecosystem is still narrow but shows signs of broadening; particularly if regulatory confidence and transparency improve.
Note: FX access and convertibility remain tightly managed by NBE.
5. Secondary and OTC Market
Fixed income trades OTC, governed under ECMA Directive No. 1009/2024
Ethiopian Securities Exchange launched in 2024, but bonds remain off-exchange
Investors trade via licensed broker-dealers registered with ECMA
Bid/offer quotes accessed through broker networks or financial outlets
Settlement handled by NBE’s Central Securities Depository (CSD)
6. Recent Trends
Since 2024, Ethiopia has introduced medium-term bonds with tenors of 3–5 years and made significant progress in onboarding both institutional and retail investors via CDS accounts. Structural reforms aimed at FX unification and liberalization are also underway. These changes are being supported by the return of an IMF program, which ties disbursements to debt sustainability and transparency benchmarks. Meanwhile, Ethiopia is in active restructuring talks for both its Eurobond and bilateral loans.
Insight: These shifts point to a government eager to regain investor trust, though policy execution and macro stability remain key to momentum.
Source: National Bank of Ethiopia (2025), Capital Ethiopia. 91-day and 182-day yields are estimated based on recent auction trends.
Note: Yields for 91-day and 182-day Treasury bills are estimated based on recent auction trends and policy trajectory. The 91-day T-bill is approximated at 15%, drawing from previous weighted averages (e.g., 13.9% reported in late 2024) and ongoing monetary tightening. The 182-day yield is estimated at 16%, positioned as a midpoint between the 91-day and the most recently confirmed 364-day yield of 17.7% (February 2025, National Bank of Ethiopia). These estimates aim to reflect the current shape of Ethiopia’s short-end yield curve under inflationary pressure and interest rate adjustments.
7. Risk Assessment
Sustainability: High risk of external debt distress (IMF 2024)
FX Risk: High – multiple exchange rates; convertibility constraints
Liquidity Risk: Moderate – domestic market still shallow
Governance Risk: Improving – ECMA and CSD structure operational
Credit Ratings (2025):
Moody’s: Caa3
S&P: CCC– (on watch)
Fitch: RD (restricted default – foreign currency)
8. Opportunities & Reforms
Full rollout of the OTC bond trading framework under ECMA
Strengthening of CSD transparency and public data access
Possible diaspora bond issuance to diversify investor base
Scope to launch green bonds or infrastructure-linked securities
FX market reform may eventually allow for offshore participation
9. Impala Market Take
Ethiopia’s bond market is under construction, anchored by legal reforms like the Capital Market Proclamation No. 1248/2021 and new directives enabling OTC trading, settlement via the Central Securities Depository, and auction participation through licensed brokers.
While the regulatory foundation is credible and the roadmap is clear, investors must navigate significant macroeconomic risks, operational opacity, and tight FX controls. The market lacks deep liquidity and real-time price discovery, but it is evolving, gradually expanding tenor profiles, onboarding new investors, and engaging with IMF-backed reforms.
This is not yet a trader’s market. It is a frontier opportunity for long-term, strategic investors. Those who engage early, build strong broker relationships, and monitor policy closely may capture early-mover advantage in one of Africa’s most ambitious sovereign debt overhauls.
10. Annexes
Treasury Auction Schedules (via MoF or CSD portals)
Legal Documents:
👉 Like what you read? Subscribe to Impala Market for sharp, weekly bond insights across Africa.
Disclaimer: Impala Market is a private information-sharing platform. It is not a licensed securities exchange or trading platform. Indicative prices shared are not offers to the public.